What Is An Domain Name? Published: 24 Dec, 2022
What Is An Domain Name?
A domain name is a text string that corresponds to an alphanumeric IP address and is used to visit a website from client software. A domain name is just the text that a user types into their browser to access a specific website. For instance, Google's domain name is “Google.com".
Although a website's actual address is a complicated IP address, such as 192.055.211.25, DNS allows visitors to type in human-friendly domain names and be directed to the websites they are looking for. A DNS lookup is the term for this procedure.
What components make up a domain name?
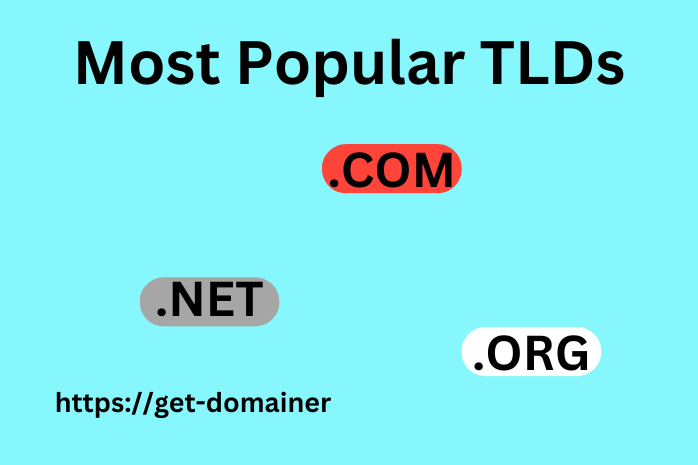
Usually, two or three elements, each separated by a dot, make up domain names. The identifiers in domain names are ordered from most generic to most particular when read from right to left. The top-level domain is the area of a domain name to the right of the last dot (TLD). These include "generic" TLDs like ".com," ".net," and ".org," as well as regional and national TLDs like ".uk" “in” “us” and ".jp."
The second-level domain (2LD) is the domain level that comes after the top-level domain (TLD), while the third-level domain is the domain level that comes after the 2LD (3LD). Let's examine a few instances:
For the "google.com" domain of Google in the US:
The TLD (most general) is ".com," and the 2LD is "google" (most specific)
But for the domain name "google.co.uk" for Google UK:
The TLD (most generic) is ".com," and the 2LD is ".co"
The 3LD (most specific) is "google"
The 2LD in this instance specifies the kind of business that registered the domain (.co in the UK is for sites registered by companies).
What distinguishes a domain name from a URL?
A uniform resource locator (URL), commonly referred to as a web address, contains the domain name of a website together with other information like the protocol and the path. For instance, in the URL "https://get-domainer.com/blog/," the domain name "get-domainer.com" is the domain name, "https" is the protocol, and "/blog/" is the path to a specific page on the website.
Who manages domain names?
All domain names are controlled by domain registries, which assign domain name reservations to registrars. There are already over 300 million registered domain names, and anyone who wants to construct a website can register one with a registrar.
How to keep a domain name secure
Once a domain name has been registered with a registrar, it is the registrar's responsibility to notify the registrant when their domain is about to expire and give them the choice to renew, saving them from losing their domain name. When a user's domain name expires, some registrars will profit from it by buying it as soon as it becomes available and selling it back to the original registrant at a significant price. Selecting a registrant who is reliable and honest is essential to preventing these unscrupulous practices.